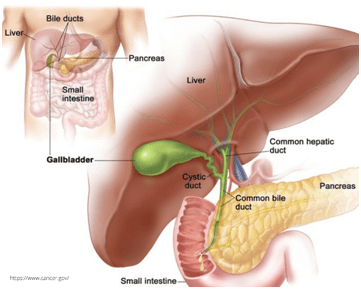
Gallstones are complex collections of the digestive fluid in the gallbladder that can develop over time. Humen’s gallbladder is the tiny organ located directly under the liver on the right part of your belly. Bile is the fluid helping your digestion stored in the gallbladder. It gets discharged into the small intestine.
Gallbladder stones can develop as tiny as a grain of sand. It can also be as big as a golf ball. Some people grow one gallstone at a time, while others acquire many gallstones at once.
Gallstones typically necessitate gallbladder removal surgery for those who have symptoms. Gallstones that do not produce any symptoms do not require treatment at all.
Many people in Mumbai suffer from gallbladder stones and related complications. So, it is always better to consult with your Bariatric & GI Laparoscopic surgeon in Mumbai for the treatment options.
Now, let us see the causes of gallbladder stone development:
Gallstones aren’t known to have a cause for development. Gallstones are thought to form when:
- There is too much cholesterol in your bile. Usually, enough molecules are present in your bile to break down the cholesterol released by your liver. However, if the liver breaks down more cholesterol than your bile can break down, the extra cholesterol may crystallize and create stones.
- There is too much bilirubin in your bile. It is a substance generated by your body when red blood cells are broken down. Cirrhosis of the liver, biliary tract infections, and some blood diseases cause your liver to produce too much bilirubin. An excess of bilirubin secretion causes gallstones and related complications.
- There can be a time when your gallbladder is not emptying properly. Bile can get extremely concentrated if your gallbladder isn’t emptying fully or frequently enough, which can lead to gallstone development.
Diagnosis
Gallstones and their consequences are diagnosed using the following tests and procedures:
Ultrasound of abdomen: It is the most frequent test for detecting indications of gallstones. A device (transducer) is moved back and forth over your stomach area during abdominal ultrasonography. The transducer delivers impulses to a computer, which generates pictures of your abdomen’s structures.
Ultrasound through the endoscope (EUS): A thin, flexible tube (endoscope) is passed into your mouth and your digestive system during EUS. A tiny ultrasound instrument (transducer) creates sound waves that generate a precise picture of the surrounding tissue in the box. This technique can assist in detecting little stones that an abdominal ultrasound may miss.
Other types of imaging examinations include –
- Oral cholecystography,
- Computed tomography (CT),
- Hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid (HIDA) scan,
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP),
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
Tests of the blood: Gallstones can cause infections, like jaundice, pancreatitis, and other problems, which can be detected by blood testing. In many cases, these detections lead to the main complication that is gallbladder stone.
So, what are the treatment options available?
Gallstones that do not produce symptoms in the majority of people will never require treatment. Based on your symptoms and the findings of diagnostic tests, your doctor will assess if gallstone therapy is necessary.
Your doctor may advise you to be on the lookout for signs of gallstone problems, such as worsening pain in your upper right abdomen.
As per Dr. Harsh Sheth – Bariatric & GI Laparoscopic surgeon in Mumbai, gallstones can be treated in various ways.
Surgery: Your doctor may prescribe surgery to remove your gallbladder. The gallbladder is removed during surgery (cholecystectomy). As a result, your bile comes directly through your liver and goes into the small intestine.
You don’t need your gallbladder to survive, and removing it does not affect your capacity to digest food. However, gallbladder removal might induce diarrhea for some patients. But you do not need to worry about it as it is curable.
Gallstone-dissolving medications: Oral medications may aid in the dissolution of gallstones. However, this could take months or years of treatment to remove your gallstones in this method, and if treatment is discontinued, gallstones would most likely develop again.
Medication may not always work in the case of gallbladder stones. Gallstones medications are seldom utilized and are only prescribed for those who are unable to undergo surgery.