The inflammation of the appendix is known as appendicitis. Although appendicitis can affect anyone, people between ten to thirty years are mostly affected.
The appendix is a tiny pouch that protrudes from the colon. It is located in the lower right corner of the abdomen. If it gets infected, it causes excruciating pain. In most cases, the inflammation worsens, causing more pain and necessitating urgent surgery.
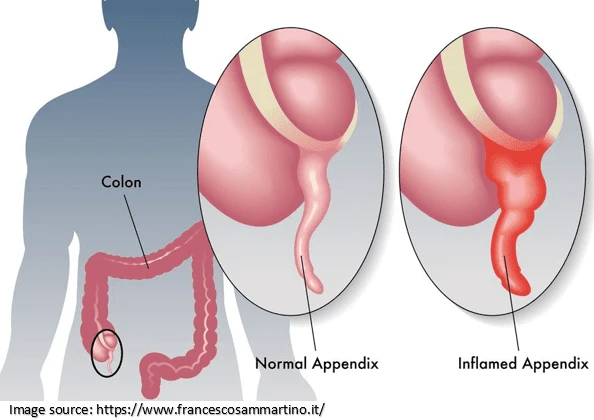
According to Dr. Harsh Sheth, a proficient laparoscopic and GI bariatric surgeon in Mumbai, the appendix can leak bacteria and infect your entire belly if it is not removed on time. It also poses a severe risk to your life. The surgical removal of the appendix is known as appendectomy.
Moreover, Dr. Harsh Sheth offers advanced and minimally-invasive appendix treatment in Mumbai. He is renowned for his expertise in gastrointestinal surgeries, upper GI surgery, and weight loss surgery in Mumbai.
In this article, we will learn when your appendix requires surgical removal, i.e., appendectomy.
First, let’s know about,
Steps Involved in Appendectomy
According to Dr. Harsh Sheth, one of the leading laparoscopic GI and weight loss surgeon in Mumbai, appendectomy is performed under spinal or general anesthesia.
- Spinal anesthesia: It involves the injection of medication into your back to make you numb below the waist. Additionally, a sleep aid may be given to you.
- General anesthesia: Once the doctor administers general anesthesia, you won’t feel any pain during the procedure because you will be asleep.
- Appendectomy Procedure:
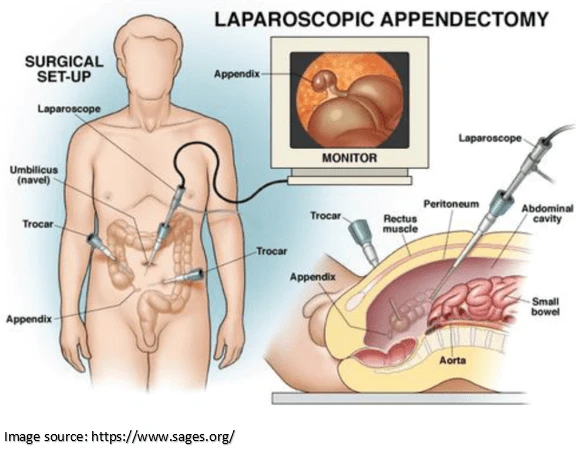
The surgeon may remove the appendix by making an incision in the lower right corner of your belly. This is an open appendectomy.
Dr. Harsh Sheth is an expert in laparoscopic gastrointestinal procedures.
Now, let’s discuss,
Signs and Symptoms of Appendicitis
The most common sign of appendicitis that might indicate you need surgery on your appendix includes:
Moving, sudden abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is the most typical indicator of appendicitis. The sudden onset of abdominal pain may indicate that you need surgery. Many patients report that their abdominal pain changes or moves.
As the condition worsens, the pain typically moves, starting close to the navel and moving to the lower right abdomen. When a pregnant woman has appendicitis, the organ shifting typically causes pain on the upper right side of the body.
Moderate fever
Numerous medical conditions, including appendicitis, can cause fever. The majority of patients typically develop a low-grade fever as the condition worsens. If there are additional symptoms, such as abdominal pain, the fever is not a sign of appendicitis.
When you cough or make any jarring movements, you might feel pain. Fever can be a warning sign; if it continues or gets worse, you must seek medical attention.
Nausea and Vomiting
Vomiting and nausea are signs of many diseases and health issues, particularly gastrointestinal infections. It may indicate appendicitis if you suddenly feel nauseous or vomit for no apparent reason.
An appendix surgery may be necessary if nausea and vomiting are present in addition to other symptoms like pain. These are indications that you should see a doctor right away.
Loss of Appetite
If you have appendicitis, thinking about food is the last thing on your mind. However, loss of appetite may result from severe stomach pain. Coupled with other symptoms, a lack of appetite may indicate that surgery is necessary. Flatulence, abdominal bloating, diarrhoea, and constipation are possible symptoms.
Appendectomy / Appendix Surgery
- Appendicitis cannot be prevented, but it can be easily treated with an appendectomy. Usually, the condition advances quickly, and if left untreated, it may be fatal.
- Laparoscopic appendectomy is the most preferred procedure, as it is less invasive and has a quicker recovery time than open appendectomy. The laparoscopic procedure also causes less pain and scarring.
However, an open appendectomy might be required to stop the infection from spreading if the appendix bursts. - Avoid using laxatives, enemas, heating pads, or other at-home remedies to treat symptoms. If you experience appendicitis symptoms, get medical attention right away.
- An infected appendix must be treated immediately. The appendix can rupture and pose a life-threatening medical emergency if prompt removal is not done. It may occur 48 to 72 hours after the onset of the symptoms.
- The patient’s age and the appendix’s position are often factors in the pain’s location. In addition to examining your abdomen, your doctor may conduct a pelvic and rectal exam.
They may recommend other tests as well:
- Blood tests, such as a white blood cell (WBC) count, to check the presence of any infection.
- Since other illnesses can produce the same or similar symptoms, the doctor may suggest a CT scan or ultrasound to ensure the appendix is the problem.
Your surgeon will then determine whether you require surgery after reviewing your symptoms, the findings of the physical examination, and the results of any medical tests.
Risks Associated with Appendectomy
Any surgical procedure carries some risks in general. Similarly, appendectomy has the following risks:
- Anesthesia and surgical risks
- Reaction to drugs
- Breathing issues
- Bleeding
- Blood clotting or infection
Below are the possible risks of an appendectomy following a ruptured appendix:
- Pus build-up (abscess), which may require drainage and antibiotics
- Infection at the incision site
Recovery After Appendectomy
After surgery, most patients go home in one to two days. After leaving the hospital, you can resume your regular activities, though it might take a few weeks to return to your previous energy level.
You will probably recover faster if you undergo laparoscopic surgery. However, recovery is more complex and takes longer if your appendix ruptures or an abscess develops.
The absence of an appendix has no known adverse effects on your health.