While pancreatic stones are commonly associated with gallbladder issues, it is possible to develop them even without a gallbladder. Understanding the complexities of this condition and the available treatment options is crucial for patients seeking relief.
Pancreatic stones without gallbladder present a unique set of challenges that require specialized expertise for successful management. Dr. Harsh Sheth, regarded as one of the best bariatric surgeon in Mumbai, brings his exceptional skills and knowledge to the table. He offers cutting-edge and minimally invasive treatments for gastrointestinal conditions, including pancreatic stones.
In this blog, we will delve into the topic of pancreatic stones without gallbladder, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatment options.
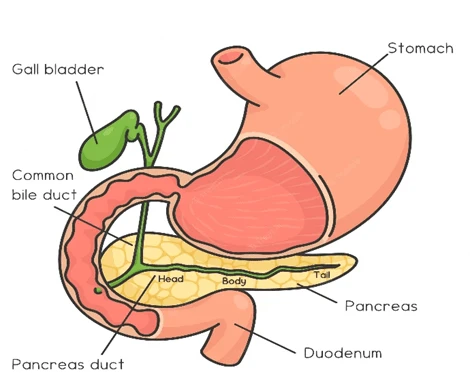
What is the connection between the gallbladder and the pancreas?
The gallbladder and pancreas are two distinct organs in the digestive system. But they work closely together to aid in digestion. The gallbladder stores and releases bile, a substance produced by the liver. It helps break down fats in the small intestine.
On the other hand, the pancreas produces digestive enzymes that aid in the breakdown of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. A common bile duct connects the gallbladder and pancreas. It allows the release of bile and pancreatic enzymes into the small intestine.
Understanding Pancreatic Stones
Pancreatic stones are solid formations that can develop within the pancreatic ducts. They are typically composed of calcium, bile salts, and other substances found in the digestive juices.
Can you get pancreatic stones without a gallbladder?
While the gallbladder plays a significant role in the formation of gallstones, it does not directly influence the formation of pancreatic stones. Pancreatic stones can develop independently within the pancreas. These stones usually comprise calcium deposits and other substances that can block the pancreatic ducts, leading to complications.
Symptoms
Pancreatic stones can cause symptoms similar to those experienced by individuals with gallstones or pancreatitis. These may include:
- Abdominal pain: Persistent pain in the upper abdomen, often radiating to the back.
- Digestive issues: Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea may occur due to impaired digestion.
- Weight loss: A decrease in appetite and unintended weight loss might be observed.
Causes
- Pancreatic duct obstruction: Blockage or narrowing of the pancreatic duct can lead to the accumulation of digestive juices, resulting in the formation of stones.
- Altered bile flow: Without a gallbladder, bile flow can be disrupted, causing changes in the composition and function of digestive juices. This imbalance may contribute to stone formation.
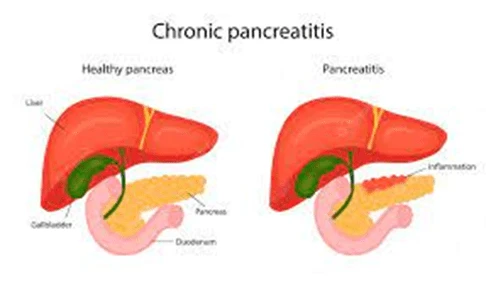
- Pancreatitis: Recurrent or chronic inflammation of the pancreas is known as pancreatitis. Regardless of gallbladder status, it can increase the risk of pancreatic stone development.
- Other causes: In some cases, genetic factors and metabolic disorders may also contribute to the development of pancreatic stones.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing pancreatic stones without a gallbladder requires a comprehensive evaluation. Your healthcare provider may employ the following diagnostic procedures:
1. Imaging tests:
Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI can provide detailed images of the pancreas and detect the presence of stones.
2. Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) or End-ultrasound (EUS):
This procedure involves the insertion of a thin, flexible tube with a camera through the mouth and into the digestive system. It helps examine the pancreatic ducts and remove or dissolve the stones.
Pancreas Stone Treatment Options
Treating pancreatic stones without a gallbladder typically focuses on managing symptoms, relieving pain, and preventing complications. They can be treated using surgical and non-surgical methods.
The appropriate treatment option depends on factors like the severity of the condition, the size and location of the stones, and the patient’s overall health.
Dr. Harsh Sheth, one of the leading GI laparoscopic and weight-loss surgeon in Mumbai, specializes in assessing individual cases and recommending the most suitable treatment options.
Let’s explore both non-surgical and surgical pancreas stone treatments:
Non-Surgical Treatments:
1. Medication
Your doctor may prescribe medications like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation caused by pancreatic stones. However, the stones eventually require surgical treatment.\
2. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL)
Once fragmented, the stones can pass naturally through the digestive system. ESWL is generally effective for smaller stones and may require multiple sessions for complete clearance. This usually has to be coupled with ERCP and stenting
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
Surgical Intervention:
1. Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP):
It is a minimally invasive pancreas stone removal procedure. It combines endoscopy and X-ray imaging to locate and remove pancreatic stones.
The surgeon inserts an endoscope through the mouth into the small intestine. They inject a contrast dye to visualize the pancreatic ducts and identify the stones. Then, the surgeon uses special tools to remove or break the stones, restoring normal pancreatic juice flow.
Surgical Intervention:
Open or conventional pancreas stone operation involves a large abdominal incision to directly access the pancreas and remove the stones.
Laparoscopic pancreatic stone surgery is a minimally invasive procedure involving making small incisions, specialized instruments and a camera that guides the surgeon in removing the stones. Dr. Harsh Sheth is highly skilled in performing conventional and laparoscopic gastrointestinal surgeries, including pancreatic stone removal. Stone removal is usually accompanied by decompression of the pancreatic duct by creating a new opening between the duct and the intestines.
Can pancreatic stones recur even after treatment?
Pancreatic stones can recur even after treatment. Therefore, addressing the underlying causes and adopting preventive measures is crucial. Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor the condition and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan if required.
Things to avoid if you have no gallbladder
If you have no gallbladder, avoiding high-fat and greasy foods is essential, as they can cause discomfort and digestive issues. Additionally, it is advisable by Dr. Harsh Sheth leading weight loss surgeon in Mumbai to limit alcohol consumption and maintain healthy body weight. A balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, can help support overall digestive health.

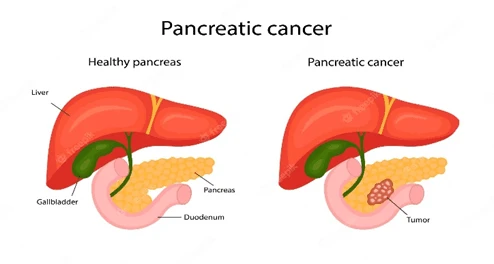
Can pancreatic stones increase the risk of pancreatic cancer?
Pancreatic stones do not directly increase the risk of pancreatic cancer. But some underlying conditions associated with pancreatic stones development, such as chronic pancreatitis, may be linked to an increased risk. Regular screenings and discussions with a specialist can help identify and manage potential risks.
Outlook
Pancreatic stones without a gallbladder are rare but can cause significant discomfort and complications. If you experience symptoms suggestive of pancreatic stones, regardless of gallbladder status, it is crucial to consult an expert like Dr. Harsh Sheth, a bariatric surgeon in Mumbai for a thorough evaluation and appropriate management. Early diagnosis and treatment can help alleviate symptoms, reduce the risk of complications, and improve your overall quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q:1 Is a stone in the pancreas serious?
A: Yes, a stone in the pancreas can cause severe complications, including chronic pain, inflammation, and digestive problems. Timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial to manage this condition effectively.
Q:2 Can pancreatic stones be prevented?
A: While it may not be possible to prevent all cases of pancreatic stones, adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing underlying conditions, and following your doctor’s advice can help reduce the risk.
Q:3 What is the prognosis for individuals with pancreatic stones without a gallbladder?
A: The prognosis for individuals with pancreatic stones without a gallbladder depends on several factors, including the severity of the condition, the underlying causes, and the response to treatment. With proper care and management, many individuals can experience significant improvements in their symptoms and overall well-being.
Q.4 Can gallbladder removal affect the pancreas?
A: Gallbladder removal itself does not directly affect the pancreas. However, it may lead to changes in bile flow and digestive enzymes. It can influence the function of the pancreas and potentially contribute to the formation of pancreatic stones.
Q:5 What foods should you avoid after gallbladder removal?
A: After gallbladder removal, avoiding high-fat and greasy foods and spicy and fried foods is advisable. These can cause digestive discomfort and may lead to complications. A balanced diet focusing on lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is recommended for optimal digestive health.